CT3680 Multi-Delay Module V2
Reference and Development Guide
 |
Overview
The Cabintech CT3680 is a hybrid module that implements from 1 to 4 flexible, configurable audio delay lines. This module can be used by system designers to create many different delay-based effects (reverb, echo, chorus, flanger, etc.) using traditional analog feedback paths, filters, and modulation techniques. Although the CT3680 is digital at its core, all inputs and outputs are analog -- no programming or digital logic design is required and it integrates easily into an analog signal flow. The CT3680 uses a fixed sampling rate that is independent of delay time, producing consistently high quality audio at any delay setting.
The CT3680 is designed to be easy to use with simple analog audio inputs and outputs, control voltages to set parameter values (such as delay time), and a single +5V power supply. The small module size (22x38mm, 0.9”x1.5”), surface mount edge pins, and through-hole adapter options provide flexibility for mechanical fitment into small spaces and optimize the use of PCB board space.
Audio Inputs/Outputs
The CT3680 has 4 analog audio inputs, and 4 analog audio outputs. The relationship between the inputs and outputs and delay times is controlled by the selected configuration settings. All audio inputs and outputs are line level (2.5V peak), single ended AC coupled for easy integration into an analog signal chain. Traditional analog effects circuits with filtering, modulation, and gain control can be used to create feedback paths for various types of effects.
Configuration
The configuration options control the number of independent delays lines (“channels”) and the maximum delay times they have. Each channel has 1 audio input and 1 or more outputs (“taps”). Each tap is an audio output with an independent delay control. For example, a channel with 2 taps would have one input and two outputs. The outputs are both delays of the same input, but with different delay times, each controlled with a separate CV (control voltage). There are many possible configurations of channels and taps. For example, one of the configurations is 2 channels with 2 taps each:
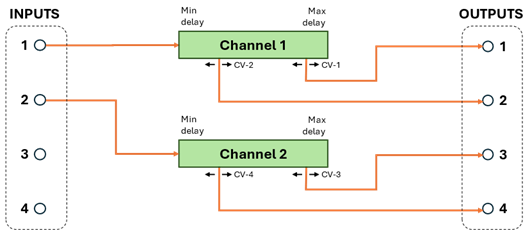
In this configuration, output 1 will be a (variable) delay of input 1. The amount of delay at output 1 is set by a control voltage (CV-1). Output 2 is also a variable delay of input 1, with its own control voltage (CV-2) which sets the delay of output 2. The delays at outputs 1 and 2 are both of the same signal at input 1 but are independently variable. Likewise, outputs 3 and 4 are independent delays of the signal at input 2, controlled by CV-3 and CV-4 respectively. A configuration like this might be used in a true-stereo effect that requires (at least) 2 separate channels of delay.
Another configuration consists of 3 independent delay lines, 2 of which have a single delayed output, and 1 has two delayed outputs (taps):
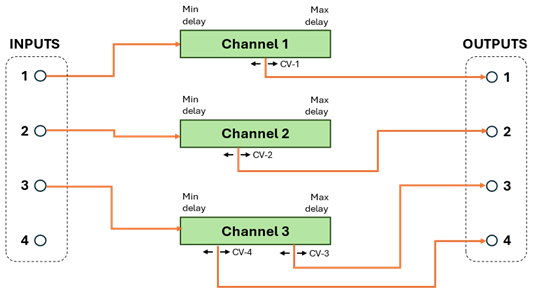
The different configurations can be useful for constructing different types of effects including stereo and effects that utilize multiple delay lines.
Configuration is done with 4 input pins that choose between different “programs”, each of which defines a specific configuration. In addition, 5 “option” input pins control additional features depending on the selected program. See Program Selection on page 12 for a description of all the available programs.
Additional inputs select the audio sampling rate (48kHz, 32kHz, 24kHz, 12kHz). Lower sampling rates allow for longer delay times. The sampling rate remains fixed at the selected rate (e.g. sampling rate is not used to vary the delay time as in traditional BBD devices). (See Sampling Rate Selection on page 11)
Delay Control
The selection of configuration and sampling rate defines the minimum and maximum delay of each channel in the configuration. The taps (outputs) for that channel can have any delay time between the min and max, and the delay time can vary dynamically by use of control voltages (CVs).
A delay CV is an input voltage in the range of 0.0V to 3.3V. When the CV is at 0.0V then the corresponding output is at the minimum delay. When the CV is at the maximum of 3.3V then the output is at the maximum delay. Voltage levels between 0.0 and 3.3 form a linear scaling of delay time between min and max. For example, the following channel configuration has 4 taps controlled by CV-1 through CV-4. With a sampling rate of 48kHz this channel has a max delay of 682ms and a min delay of 0.3ms.
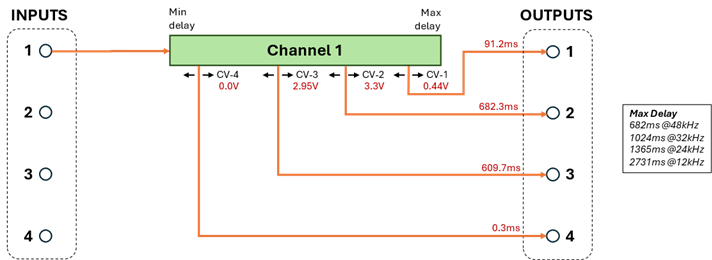
With the control voltage values shown, the outputs have the delays shown[1]. Note that the lines as drawn in the diagram are conceptual and not drawn in proportion to the actual delay time. E.g. the line for output 1 is drawn to the right of channel 2 on the green channel bar (closer to Max delay), but actually has a shorter delay time. The CV for any output can select any delay time in the range from min to max, independent of all other outputs.
Also see Setting Delay Times on page 27.
Additional Features
Some programs (configurations) support additional features. These features are optional and enabled using the 5 OPTION input pins. See the individual program descriptions to see what features are supported in which programs.
·
Simulated aliasing: Some programs support
the ability to simulate sampling-rate aliasing similar to
the aliasing distortion that occurs in BBD devices when run at lower clock
(sampling) rates. In some effects this distortion is desirable and is part of
the overall sonic design. The amount of aliasing distortion can be manually
controlled by CV or automatically determined by the delay settings. Aliasing
distortion is disabled by default. (See Aliasing Feature
on page 25).
·
Mono-to-stereo effects: Some programs
perform mono-input to stereo-output conversion using a Haas delay effect. The left-right
spread of the stereo effect can be varied and is controlled by a CV input.
· Chaining: Multiple CT3680 modules can be “chained” together to achieve very long delay times and more inputs and outputs. Audio signals are passed digitally through the chain so there is no loss in fidelity no matter how many modules are linked together. (See Chaining Multiple Modules on page 27).
Design Requirements
The CT3680 is designed to minimize external component requirements and integrate easily to PCB effects designs. The CT3680 requires no external clock and is powered by +5V. All CV signals are +3.3V maximum (see Specifications and Maximum Ratings on page 7). A +3.3V reference is made available on an output pin to aid in generating CV signals. All audio analog inputs and outputs are single-ended, 2.5V full scale, and AC coupled. Clipping is detected and signaled on an output pin and an onboard LED.
The physical package is a 48 pin surface mount castellated edge pin module. It can easily be hand soldered or soldered in automated systems. A 48-pin standard DIL spacing through-hole adapter is available for through-hole PCB designs.
Features
· Input pin selectable configuration for 1, 2, 3, or 4 independent delay lines in multiple configurations.
· Maximum delay of 2.7 seconds (divided between all delay lines)
· Minimum delay time of 0.3ms
· 6 CV inputs to control delay and other parameters
· Digitally chainable up to 5 modules with total max delay of 13.5 seconds
· +5V 170mA power supply
· Reverse voltage protection
· 4 analog audio inputs
· 4 analog audio outputs
· Internal digital sampling at 48kHz (default), 32kHz, 24kHz, or 12kHz
· No external clock is required
· Clipping-detected output signal and on-board clipping LED
· Optional simulated manual and automatic aliasing distortion
· Optional mono-to-stereo conversion on some programs
· Emulation of any BBD model MN3001 to MN3011 plus SAD512, SAD1024, TDA1022, V3205, V3207, V3208
· Castellated edges for direct soldering to a PCB (through-hole adapter is available)
· Updatable firmware (“programs”)
Pinout
|
Pin |
I/O |
Symbol |
Description |
|||||||||||||||
|
1 |
In |
AUDIO_IN_1 |
Audio input 1 |
|||||||||||||||
|
2 |
In |
AUDIO_IN_2 |
Audio input 2 |
|||||||||||||||
|
3 |
Out |
AUDIO_OUT_1 |
Audio (tap) output 1 |
|||||||||||||||
|
4 |
Out |
AUDIO_OUT_2 |
Audio (tap) output 2 |
|||||||||||||||
|
5 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
6 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
7 |
In |
LINK_1CH |
Number of
channels linked in a secondary module (internal
pullup) |
|||||||||||||||
|
8 |
- |
5V |
+5V supply |
|||||||||||||||
|
9 |
- |
5V |
+5V supply |
|||||||||||||||
|
10 |
- |
I2C_SCL |
I2C connector pins for firmware updating (see Firmware Updates on page 32). Leave unconnected when not used for updates. |
|||||||||||||||
|
11 |
- |
I2C_SDA |
||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
In |
PGM0 |
Bit 0 (lsb) of program number (internal pulldown) |
|||||||||||||||
|
13 |
In |
PGM1 |
Bit 1 of program number (internal pulldown) |
|||||||||||||||
|
14 |
In |
PGM0 |
Bit 0 (lsb) of program number (internal pulldown) |
|||||||||||||||
|
15 |
In |
PGM3 |
Bit 3 (msb) of program number (internal pulldown) |
|||||||||||||||
|
16 |
Out |
REF_3V3 |
+3.3V output reference (10mA max) |
|||||||||||||||
|
17 |
In |
VC_DELAY_4 |
Set delay time within the global time scale |
|||||||||||||||
|
18 |
In |
VC_DELAY_3 |
Set delay time within the global time scale |
|||||||||||||||
|
19 |
In |
VC_DELAY_2 |
Set delay time within the global time scale |
|||||||||||||||
|
20 |
In |
VC_DELAY_1 |
Set delay time within the global time scale |
|||||||||||||||
|
21 |
In |
CV_SCALE_MAX |
Global scalar for maximum delay time |
|||||||||||||||
|
22 |
In |
CV_SCALE_MIN |
Global scalar for minimum delay time |
|||||||||||||||
|
23 |
- |
GND |
Ground |
|||||||||||||||
|
24 |
- |
GND |
Ground |
|||||||||||||||
|
25 |
In |
RESET |
Pull low for 1ms or longer to reset (internal pullup) |
|||||||||||||||
|
26 |
In |
RATE_1 |
Set audio sampling rate, takes effect on next reset or power on (internal pullup)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
27 |
In |
RATE_0 |
||||||||||||||||
|
28 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
29 |
Out |
CLIPPING |
Driven high when one or more inputs are at full scale. 5mA max draw. This also drives the on-board clipping LED. |
|||||||||||||||
|
30 |
In |
OPTION_5 |
Digital control inputs (usage depends on the selected program). These inputs have an internal pullups and register as HIGH when disconnected. |
|||||||||||||||
|
31 |
In |
OPTION_4 |
||||||||||||||||
|
31 |
In |
OPTION_3 |
||||||||||||||||
|
33 |
In |
OPTION_2 |
||||||||||||||||
|
34 |
In |
OPTION_1 |
||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
36 |
In |
PRIMARY |
Sets this module mode to PRIMARY (high) or SECONDARY (low). See Chaining Multiple Modules on page 24. Changes take effect on next RESET or power on. (internal pullup) |
|||||||||||||||
|
37 |
Out |
LINK_OUT |
N.C on single modules or the last module in a multi-module configuration. Connected to downstream module’s LINK_IN in multi-module configurations. |
|||||||||||||||
|
38 |
In |
LINK_IN |
N.C. on single modules or the primary module in a multi-module configuration. Connected to the upstream module’s LINK_OUT in multi-module configurations. |
|||||||||||||||
|
39 |
In/Out |
LINK_BUS_2 |
N.C. on single modules. Connected to all module’s LINK_BUS2 pins in multi-module configurations. |
|||||||||||||||
|
40 |
In/Out |
LINK_BUS_1 |
N.C. on single modules. Connected to all module’s LINK_BUS1 pins in multi-module configurations. |
|||||||||||||||
|
41 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
42 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
43 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
44 |
- |
N.C. |
Leave unconnected |
|||||||||||||||
|
45 |
Out |
AUDIO_OUT_4 |
Audio (tap) output 4 |
|||||||||||||||
|
46 |
Out |
AUDIO_OUT_3 |
Audio (tap) output 3 |
|||||||||||||||
|
47 |
In |
AUDIO_IN_3 |
Audio input 3 |
|||||||||||||||
|
48 |
In |
AUDIO_IN_4 |
Audio input 4 |
Notes:
N.C. pins must be left
unconnected.
Unused audio and CV inputs
should be tied to ground to minimize noise.
Unused outputs should be left unconnected.
Specifications and Maximum Ratings
|
Item |
Symbol |
Range |
Notes |
|
Supply Voltage |
5V |
+4.5 to +5.5V |
170mA |
|
CV input voltage |
CV_* |
0 to REF_3V3 |
|
|
Audio input |
AUDIO_IN_* |
0 to 2.6V p-p |
AC coupled |
|
Audio output |
AUDIO_OUT_* |
0 to 2.5V p-p |
AC coupled |
|
Audio input impedance |
|
7-10kΩ |
|
|
Audio output load impedance |
|
5kΩ |
Min |
|
Signal to Noise Ratio |
|
> 92dB |
|
|
Noise floor |
|
|
|
|
THD |
|
|
|
|
Frequency response |
|
|
20Hz - 20kHz |
All measurements are unweighted, 48kHz sampling rate.
Sampling Rate Selection
The CT3680 (hardware version 2.0A and later) supports four sampling rates, selected by the RATE_0 and RATE_1 input pins. Changes to the sampling rate takes effect at the next RESET or power on (sample rate does not change dynamically). The choice of sampling rate defines the range of possible delays that can be achieved.
Choosing a sampling rate defines only the minimum and maximum total available delay. The actual delay at any particular output depends on the CV inputs as determined by the currently running program (see Program Selection on page 9). Unlike BBD devices, sampling rate is not used to dynamically alter (modulate) the delay time. The sampling rate stays fixed until the module is RESET or power cycled. Delay modulation is achieved by changes in the CV inputs.
By selecting a lower sampling rate, less memory is required to store (delay) samples per second, so longer delays can be achieved. This is a trade off between longer delay times and higher fidelity – audio quality decreases with lower sampling rates.
The following table shows the sampling rates and min/max delays that are selected by the RATE_1 and RATE_0 pins.
|
RATE_1 |
RATE_0 |
Sampling Rate |
Min Delay |
Total Max Delay |
|
0 |
0 |
12kHz |
1.16ms |
2.731s |
|
0 |
1 |
24kHz |
0.58ms |
1.365s |
|
1 |
0 |
32kHz |
0.44ms |
1.024s |
|
1 |
1 |
48kHz |
0.29ms |
0.682s |
“Total Max Delay” is the total delay time of all channels combined. How this total delay time is divided among the delay channels is defined by the selected program. For example, program 0 allocates all the available delay time to a single channel with 4 tap points. Program 3 divides all the delay time equally among 4 independent channels (so for example, if the sample rate is 24kHz, that program will allocate 1.37s / 4 = 344ms to each channel). See the program descriptions to see how the total available delay time is allocated for each program.
When multiple modules are chained together (see Chaining
Multiple Modules
on page 24)
all modules will operate at the same sampling rate as set on the PRIMARY
module.
Program Selection
Configuration of the module is done by selecting a “program” using the 4 PGM input pins. The selected program defines the basic topology of the delay lines (numer of channels, number of taps, etc). Additional configuration options for some programs are done through the OPTION pins. The selected program can be changed at any time. When the program is changed, the current delay buffer is cleared, the new program is loaded, and input samples begin to be processed into the delay buffer.
Upon power-up or a change in program selection, the white LED on the module will flash the program number (+1) to confirm operation of the module and the selected program. If an unused program number is selected, the LED will continuously fast-flash until a valid program is selected.
The following table is a quick summary of the available
programs. Each program is described in more detail in the following sections.
The “Max Delay Time/Ch” indicates what percentage of the total available delay
time is allocated to each channel. The total available delay time is defined by
the currently selected sampling rate (see
Sampling Rate Selection on page 8). For example, Program 1 allocates 50% of the total delay time to each of 2 channels, so if the sampling rate is 32kHz (1.02s total delay time), each channel will have a maximum delay of 1.02s / 2 = 51ms.
Summary of Programs
|
|
Program 0 1 Channel |
Program 1 2 Channels |
Program 2 3 Channels |
Program 3 4 Channels |
|
Channels |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Taps/Channel |
4 |
2 |
1 (+1 on chan 3) |
1 |
|
Max Delay Time/Ch |
100% |
50% each |
33.3% each |
25% each |
|
Aliasing Support |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
AUDIO_IN_1 |
Chan 1 input |
Chan 1 input |
Chan 1 input |
Chan 1 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_2 |
Unused |
Chan 2 input |
Chan 2 input |
Chan 2 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_3 |
Unused |
Unused |
Chan 3 input |
Chan 3 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_4 |
Unused |
Unused |
Unused |
Chan 4 input |
|
AUDIO_OUT_1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 |
|
AUDIO_OUT_2 |
Chan 1 tap 2 |
Chan 1 tap 2 |
Chan 2 tap 1 |
Chan 2 tap 1 |
|
AUDIO_OUT_3 |
Chan 1 tap 3 |
Chan 2 tap 1 |
Chan 3 tap 1 |
Chan 3 tap 1 |
|
AUDIO_OUT_4 |
Chan 1 tap 4 |
Chan 2 tap 2 |
Chan 3 tap 2 |
Chan 4 tap 1 |
|
CV_SCALE_MIN |
Global scalar minimum delay |
|||
|
CV_SCALE_MAX |
Global scalar maximum delay |
|||
|
CV_DELAY_1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 delay |
Chan 1 tap 1 delay |
Chan 1 tap 1 delay |
Chan 1 tap 1 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_2 |
Chan 1 tap 2 delay |
Chan 1 tap 2 delay |
Chan 2 tap 1 delay |
Chan 2 tap 1 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_3 |
Chan 1 tap 3 delay |
Chan 2 tap 1 delay |
Chan 3 tap 1 delay |
Chan 3 tap 1 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_4 |
Chan 1 tap 4 delay |
Chan 2 tap 2 delay |
Chan 3 tap 2 delay |
Chan 4 tap 1 delay |
|
|
Program 4 2 Chan + Stereo Eff |
Program 5 MN3011 Emulation |
Program 6 BBD Emulation |
|
Channels |
3 |
1 |
4 |
|
Taps/Channel |
1 |
6 (2 CT3680 reqd) |
1 |
|
Max Delay Time/Ch |
46% chan 1 & 2 |
682ms |
Varies by options |
|
Aliasing Support |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
AUDIO_IN_1 |
Chan 1 input |
Delay input |
Chan 1 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_2 |
Chan 2 input |
Unused |
Chan 2 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_3 |
Chan 3 input |
Unused |
Chan 3 input |
|
AUDIO_IN_4 |
Unused |
Unused |
Chan 4 input |
|
AUDIO_OUT_1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 |
Fixed delay 4 / 6 |
Chan 1 output |
|
AUDIO_OUT_2 |
Chan 2 tap 1 |
Fixed delay 3 / 5 |
Chan 2 output |
|
AUDIO_OUT_3 |
Chan 3 LEFT |
Fixed delay 2 |
Chan 3 output |
|
AUDIO_OUT_4 |
Chan 3 RIGHT |
Fixed delay 1 |
Chan 4 output |
|
CV_SCALE_MIN |
Global min delay |
Unused |
|
|
CV_SCALE_MAX |
Global max delay |
Unused |
|
|
CV_DELAY_1 |
Chan 1 tap 1 delay |
Unused |
Chan 1 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_2 |
Chan 2 tap 1 delay |
Unused |
Chan 2 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_3 |
Unused |
Unused |
Chan 3 delay |
|
CV_DELAY_4 |
Stereo field control |
Unused |
Chan 4 delay |
The following sections describe each program and how they define the channels, delay times, and various options.
Program 0
(1 Delay, 4 Taps)
This program provides a single delay line with a maximum delay time of 100% of the total available.
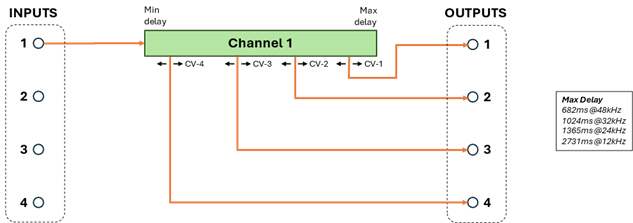
AUDIO_IN_1 is the delay line input, all other audio inputs are unused. Four delay outputs are available, each delay time independently controlled with the corresponding CV_DELAY value. The global MIN/MAX scalars apply to all taps. Note there is no required ordering of the delay taps, e.g. delay 1 could be longer than delay 3. All the taps are independently controlled by their corresponding CV delay input and changing one CV value does not affect the delay at the other taps.
This program supports aliasing (see Aliasing Feature on page 22). Only the manual aliasing mode is supported. When aliasing is enabled, CV_DELAY_4 controls both the delay of output 4 and the intensity of the aliasing effect on all audio outputs.
Program 1
(2 Delays, 2 Taps Each)
This program is 2 independent delay channels with 2 taps each. Each channel has a maximum delay time of 50% of the total available.
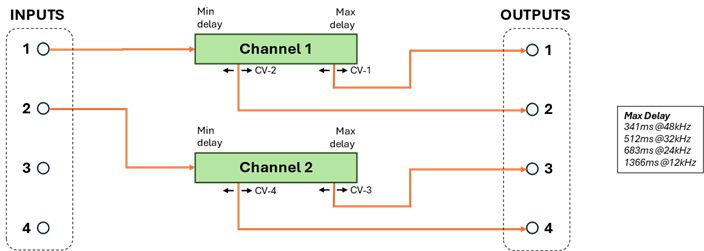
AUDIO_INPUT_1 and AUDIO_INPUT_2 are the inputs to the 2 channels, all other audio inputs are unused. Channel 1 has two taps provided at AUDIO_OUT_1 and AUDIO_OUT_2. Channel 2’s outputs are AUDIO_OUT_3 and AUDIO_OUT_4. All taps for all channels are bounded by the global MIN/MAX scalars.
This program supports aliasing (see Aliasing Feature on page 22). Only the manual aliasing mode is supported. When aliasing is enabled, CV_DELAY_4 controls both the delay of output 4 and the intensity of the aliasing effect on all audio outputs.
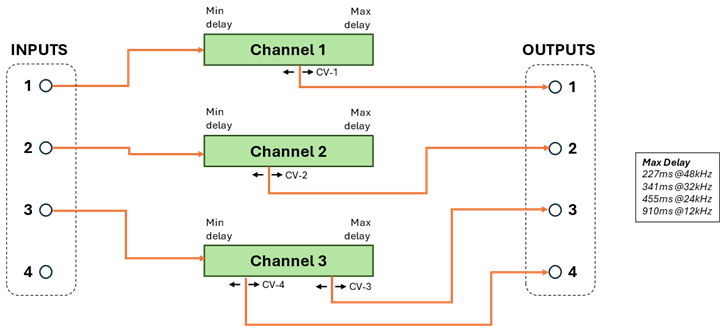
Program 2
(2 Delays with 1 Tap, plus 1 Delay with 2 Taps)
This program provides 3 independent delay channels.
The first 2 channels (AUDIO_INPUT_1/2) have a single delayed output each (AUDIO_OUT_1/2). The third channel has 2 delayed outputs (ADUIO_OUT_3/4) controlled by CV_DELAY_3 and CV_DELAY_4. The maximum delay time for each channel is 1/3 of the total available. The global MIN/MAX scalars apply to all delay times.
This program supports aliasing (see Aliasing Feature on page 22). Only the manual aliasing mode is supported. When aliasing is enabled, CV_DELAY_4 controls both the delay of output 4 and the intensity of the aliasing effect on all audio outputs.
 |
Program 3
(4 Delays with 1 Tap each).
This program provides 4 independent delay channels each with a maximum delay time of 25% total available.
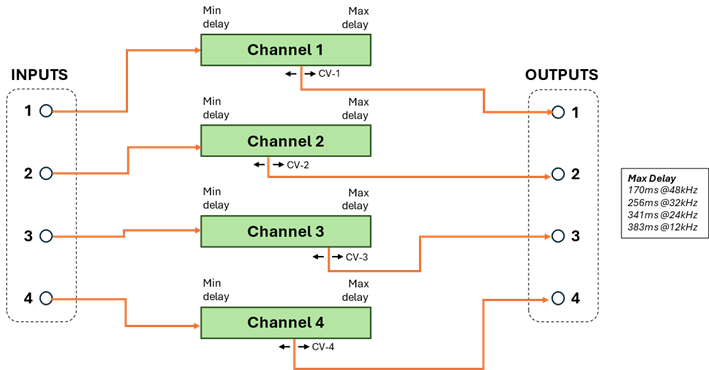
Each channel has a single delayed output controlled by the corresponding CV_DELAY_x value. The global MIN/MAX scalars apply to all delay times. This program does not support aliasing.
Program 4
(2 Delays with 1 Tap, plus a stereo effect pair output)
This program has 3 independent delay channels. The first two channels have a single delayed output, channel 3 outputs a variable stereo (Haas effect) on outputs 3 and 4 which converts the mono input to stereo output.
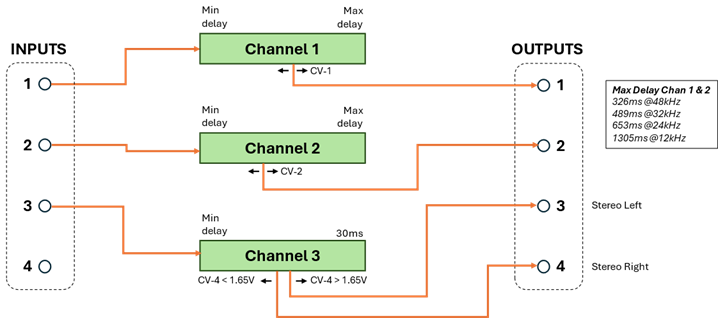
The 3rd channel has no delay but produces a Haas stereo effect output with audio outputs 3 and 4 providing the L/R stereo pair. CV_DELAY_4 is used as the effect control. When the effect control is in the center of the range (1.65v) there is no stereo effect, both output channels will have the minimum (0.3ms) delay, e.g. the outputs are mono. When the control is < 1.65v delay is added to output 4 effectively moving the stereo field left. When the control is > 1.65v delay is added to output 3 moving the stereo field right. The amount of delay added is proportional to how far the effect control voltage is from center (1.65v). The maximum added delay is 30ms (at 0v left, and 3.3v right). The global MIN and MAX scalars have no effect on outputs 3 and 4, nor does the sampling rate.
This program does not support the aliasing feature.
Program 5
(MN3011 Emulation, two CT3680 modules recommended)
This program emulates the 6-tap delay structure of the MN3011 BBD delay chip. To use the full 6-tap capability of this program requires two CT3680 modules chained together (see Chaining Multiple Modules on page 24). If only a single module is used, this program will produce the first 4 taps of the MN3011.
The 48kHz sampling rate must be selected when using this program (see Sampling Rate Selection on page 8).
This program supports aliasing (see Aliasing Feature on page 22). Only the manual aliasing mode is supported. To have consistent aliasing effects on all outputs, both modules of a 2-module configuration should have aliasing enabled and their VC_DELAY_4 lines should be tied together so the same aliasing intensity is used on all audio outputs.
MN3011 emulation is achieved by fixing the CT3680 delay tap ratios to the delay intervals of the physical MN3011 BBD chip. The 48kHz sampling rate must be selected for accurate MN3011 emulation.
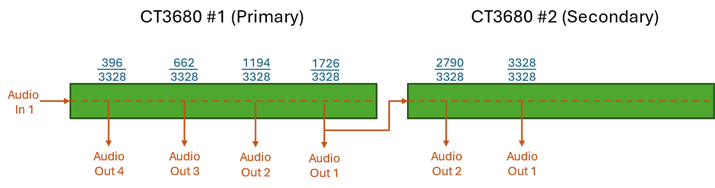
Those delay time ratios are scaled into the global MIN/MAX delay times as set by their respective CV values. When two modules are used for the 6-tap configuration, the MIN/MAX inputs of the two modules must be tied together (e.g. both modules get identical MIN/MAX CVs). This is in addition to the connections required for all module chaining configurations as described in the Chaining Multiple Modules section. If only a single module is used it will produce the first 4 tap intervals and no special hardware configuration is required.
If the aliasing feature is used with this program, the OPTION_5, and CV_DELAY_4 (alias intensity) of both modules should be tied together so that all outputs have consistent aliasing effects applied.
Since the delay intervals are fixed, the CV_DELAY_1/2/3
inputs of both modules are unused. All the output delays are determined by
mapping the MN3011 intervals into the MIN/MAX global range. The first 4 taps
are produced by the first (primary) module on AUDIO_OUT_4/3/2/1 (e.g.
the shortest MN3011 tap is produced on AUDIO_OUT_4 of the first module, the 2nd
shortest on AUDIO_OUT_3, the 3rd on AUDO_OUT_2, and the 4th
tap is on AUDIO_OUT_1). The last 2 taps are produced by the second module on
AUDIO_OUT_2/1 (5th tap on AUDIO_OUT_2 and the longest tap (6th)
on AUDIO_OUT_1). Audio outputs 3 and 4 of the second module are unused. 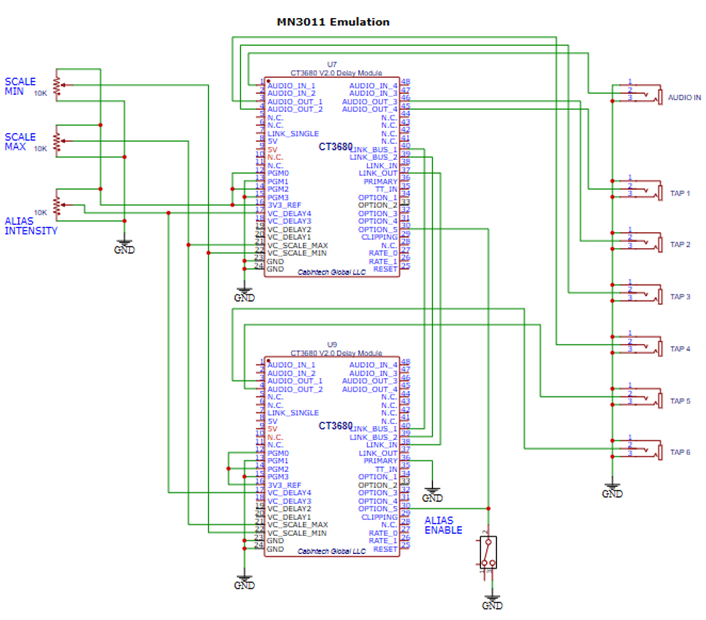
The CT3680 MN3011 emulation supports delay intervals over a wider range than the physical MN3011. At its maximum and minimum clock speeds the MN3011 supports delay ranges of 2.0-16.6ms (100kHz clock) to 19.8-166.4ms (10kHz clock). The CT3680 supports delay ranges from 0.9-5.0ms to 81-682ms. The following table shows some typical MIN/MAX settings and the resulting delay times for each output. For reference, the MN3011 delay times at minimum and maximum clock rates are also shown.
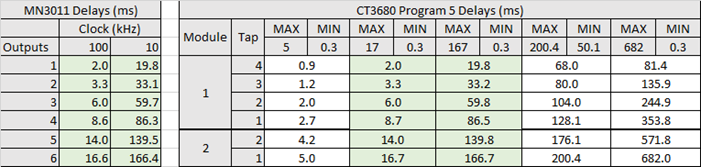
Program 6
(General BBD Emulation)
This program provides emulation of many different BBD chips including all MN30XX models MN3001-MN3010 (see Program 5 for MN3011), plus SAD512/SAD1024, TDA1022, and V3205, V3207, V3208. This program provides 4 independent delay lines, one for each audio input/output pair. Each line will emulate one of the BBD chips based on the configuration selected. See Configuration Selection below.
The 48kHz sampling rate must be selected when using this program (see Sampling Rate Selection on page 8).
Emulation consists of setting fixed minimum and maximum delay times based on the BBD datasheets. Since the min/max delay time is defined by the BBD model, the global VC_DELAY_MIN and VC_DELAY_MAX values are not used. Each of the four VC_DELAY_X inputs define the delay of a particular channel within the range defined by the BBD model. For example, a delay line configured for an MN3009 will have a minimum delay of 0.64ms (VC_DELAY_X at 0.0V) and maximum of 12.8ms (VC_DELAY_X at 3.3V).
Configuration Selection
Configurations define which BBD chips are emulated on which delay channel. 4 BBDs can be emulated at a time, in combinations defined by the configuration.
1 of 8 configurations can be chosen by the OPTION_1, OPTION_2, and OPTION_3 inputs. These form a binary number which selects one of the configurations (see table below). Each configuration emulates 4 BBD chips, each BBD on an independent delay line. For example, when configuration zero is selected (OPTION pins 3,2,1 = LOW) delay channel 1 emulates an MN3003, channel 2 is an MN3006, channel 3 is an MN3007, and channel 4 is an MN3008.
Configurations 0 through 4 define various combinations designed to provide a wide variety of delay lines in each configuration. All BBD models are represented in at least one of the configurations. Configurations 5 through 7 provide dual delay lines of 2 selected types useful for stereo applications.
The following table shows which BBDs (and associated delay times) are on which channels for each of the 8 configurations. To see which BBDs are in a particular configuration, read one column of the table. Min and max delay times are in msec.
|
|
|
Configuration selected by OPTION pins [3:2:1] |
|||||||
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
CHAN 1 |
BBD |
MN3003 |
MN3009 |
MN3006 |
MN3009 |
MN3006 |
MN3006 |
MN3001 |
MN3009 |
|
Min |
*0.16 |
0.64 |
0.32 |
0.64 |
0.32 |
0.32 |
0.32 |
0.64 |
|
|
Max |
3.20 |
12.80 |
6.40 |
12.80 |
6.40 |
6.40 |
25.60 |
12.80 |
|
|
CHAN 2 |
BBD |
MN3006 |
MN3001 |
MN3004 |
MN3007 |
V3207 |
MN3006 |
MN3001 |
MN3009 |
|
Min |
0.32 |
0.32 |
2.56 |
5.12 |
2.56 |
0.32 |
0.32 |
0.64 |
|
|
Max |
6.40 |
25.60 |
25.60 |
51.20 |
51.20 |
6.40 |
25.60 |
12.80 |
|
|
BBD |
MN3007 |
SAD512 |
V3207 |
MN3008 |
MN3005 |
MN3007 |
MN3008 |
MN3005 |
|
|
Min |
5.12 |
*0.17 |
2.56 |
10.24 |
20.48 |
5.12 |
10.24 |
20.48 |
|
|
Max |
51.20 |
170.67 |
51.20 |
102.40 |
204.80 |
51.20 |
102.40 |
204.80 |
|
|
CHAN 4 |
BBD |
MN3008 |
MN3005 |
MN3008 |
TDA1022 |
MN3005 |
MN3007 |
MN3008 |
MN3005 |
|
Min |
10.24 |
20.48 |
10.24 |
51.20 |
20.48 |
2.12 |
10.24 |
20.48 |
|
|
Max |
102.40 |
204.80 |
102.40 |
512.00 |
204.80 |
51.20 |
102.40 |
204.80 |
|
(*) BBDs with a min delay < 0.3ms will have an emulated min delay = 0.3ms (MN3003 and SAD512).
This program supports the Aliasing Feature as described on page 22. Aliasing is controlled by CV_DELAY_MIN (which is otherwise unused in this program). This program supports both manual mode and automatic mode aliasing. Manual mode (CV_DELAY_MIN between 0.0V and 3.0V) operates as described in the Aliasing Feature section – 0.0V results in no aliasing distortion, values near 3.0V result in maximum aliasing (simulating a sample rate approaching zero).
In automatic mode (CV_DELAY_MIN >= 3.0V) the amount of aliasing is automatically determined by the characteristics of the simulated BBD and the current delay setting. This is done by determining the clock speed that corresponds to the current delay setting for the simulated BBD, and applying aliasing that corresponds to that clock speed. If the determined clock speed is >48kHz the no aliasing is applied.
For example, if an MN3007 is being simulated (configuration 3, channel 2) and the CV_DELAY_2 input is set to 2.8V, then the delay of channel 2 will be 39.1ms[2]. In a real MN3007 BBD chip, this would occur at a clock speed of 23.6kHz[3]. In automatic mode an aliasing effect corresponding to 23.6kHz would be applied to channel 2. If the delay CV is changed, then the corresponding aliasing level automatically changes to track it.
Aliasing Feature
Some programs of the CT3680 support an ‘aliasing’ feature that emulates the behavior of physical BBD devices when they are run at lower clock speeds (e.g. longer delay times). Aliasing is a form of distortion caused by sampling the audio at a rate lower than 2 times the maximum audio frequency. Some delay-based systems use the aliasing distortion as part of the intended effect and consider it desirable, and in some way “authentic” to classic BBD delay effects.
The aliasing feature of the CT3680 allows the effects designer to choose how much, if any, aliasing distortion is to be introduced into the output signal, and to control it in various ways. By disabling this effect (the default state) and running the CT3680 at the 48kHz sampling rate (the default), a “clean” delay is produced with no audible aliasing. This feature should only be used if the circuit designer specifically desires some level of aliasing distortion.
In a physical BBD device, the intensity (frequency band) of the aliasing changes with the delay time (since delay time is defined by (clock) sampling rate). Since the CT3680 always samples at a fixed rate, this feature can be used to simulate the aliasing effect of any sampling rate and it can be varied (modulated) with delay time or in some other way via a CV input.
When a sampling rate below 48kHz is selected on the RATE pins, the CT3680 will also (by definition) exhibit some amount of aliasing in the audio frequency band. The lower the sampling rate, the more the aliasing effect which will be most prominent in higher audio frequencies. At less than 48kHz sampling rate, the minimum aliasing will be fixed and this aliasing feature will add additional distortion to it. Note that at 32kHz sampling, the fixed amount of aliasing is minimal. At lower rates (24kHz, 12kHz) it is much more noticeable.
The OPTION_5 pin enables aliasing mode when it is set LOW. By default (no connection on the OPTION_5 pin), the aliasing feature is disabled.
|
OPTION_5 |
Aliasing Effect |
|
N.C. |
Disabled |
|
HIGH |
Disabled |
|
LO |
Enabled |
The intensity and mode of the aliasing effect can be controlled by one of the VC inputs (which CV input is used to control aliasing is defined by the selected program – see the program descriptions). Control of the aliasing can be manual mode or automatic mode. The mode is determined by the CV input voltage range. When the CV is between 0.0V and 3.0V the aliasing is in manual mode. When the CV is 3.0 to 3.3V aliasing is automatic. Note that not all program support both modes, see the program descriptions.
Manual Mode Aliasing
Manual mode is selected with an aliasing effect VC voltage in the range 0.0V to 3.0V. The intensity is set by the value of the VC input such that an input voltage of 0.0V will cause no effect and an input voltage of 3.0V will simulate a sampling rate approaching zero (maximum aliasing distortion). The aliasing effect CV input can be set to any level of desired aliasing, or it can be varied over time or in sync with the delay settings. It must remain in the range of zero to 3.0V for manual mode control.
When manual aliasing is at its most extreme setting (approaching 3.0V) this can cause the audio to drop out because the output signal approaches DC (constant value).
Automatic Mode Aliasing
Automatic mode aliasing is selected when the aliasing effect CV input is above 3.0V (e.g. 3.0V to 3.3V). In automatic mode the intensity of the aliasing is automatically determined by the delay settings to simulate real BBD hardware in which the aliasing effect is more intense at longer delay times. See the individual program descriptions for how automatic aliasing intensity is determined. If the program does not support automatic aliasing, then alias effect CV inputs above 3.0V have the same effect as 3.0V (e.g. maximum manual aliasing).
If multiple modules are chained together, in general it is desirable that they all produce the same aliasing effect (although it is not required). To achieve that, the OPTION_5, and aliasing effect VC input of all modules in the chain should be tied together. See the Chaining Multiple Modules section on page 24.
Setting Delay Times
Delay CV Inputs
Delay times in the CT3680 are defined by CV (control voltage) inputs in the range of 0.0v to +3.3v. A minimal CV input (0.0V) indicates a minimum delay time, and a maximum CV input (+3.3V) indicates a maximum delay time. CV values between 0.0V and 3.3V define a linear scaling of delay time between the minimum and the maximum. What actual delay times those represent depends on the global delay scalars (see next section), the currently selected program (see Program Selection on page 9), and the currently selected sampling rate (see Sampling Rate Selection on page 8). The CT3680 is capable of delay times from 0.3ms to 2.7 seconds.
Global Scalars
Two CV inputs (CV_SCALE_MIN, CV_SCALE_MAX) define a global range for all delay times. All individual tap delays on all channels are scaled to be in the range of MIN-MAX. This allows individual delay CV inputs to use their full scale (0.0V to 3.3V) to cover a range of delay values that are of use for a particular application. (It would be unusual for an effect to use delay times across the full device capability). With a narrower global range, the CV tap inputs operate with more precision in the delay range of interest and makes them less susceptible to noise.
For example, if a module is to operate as a 2 channel delay with delay times between 100ms and 200ms, then program 1 would be selected since it defines a 2 channel configuration. The table in the Program Selection section shows the max capable delay time for that program is 341ms at 48kHz sampling rate. To set a global minimum delay to 100ms, the CV_SCALE_MIN would be set to (100ms/341ms)*3.3v = 0.97v. To set a global maximum of 200ms, CV_SCALE_MAX would be set to (200ms/341ms)*3.3v = 1.94v. With those settings, both delay channels are constrained to a minimum delay of 100ms, and a maximum delay of 200ms.
With those global MIN/MAX settings, the CV delay inputs (CV_DELAY_x) used to set the individual output delay times have a full scale range of 100ms to 200ms. E.g. setting CV_DELAY_1 to 0.0v would result in channel 1 tap 1 (on pin AUDIO_OUT_1) to be delayed 100ms (global MIN). Setting it to its halfway point (3.3/2=1.65v) would result in a delay time halfway between global MIN and MAX, e.g. 150ms. Setting it to full scale 3.3v results in a delay time of 200ms (global MAX).
The global MIN and MAX times apply to all channels and all taps. Note that the global MIN and MAX delay time CV inputs are really a differential pair. It is not required that VC_SCALE_MAX be greater than VC_SCALE_MIN. The lower of the two CVs defines the global minimum delay time and the higher of the two defines the global maximum delay time. If the values are the same, then all delays are constrained to that single value (or narrow range).
All CV inputs, including the global scalars, may be modulated (varied with time) to achieve various effects.
Chaining Multiple Modules
Overview
This feature allows multiple modules to be (digitally) chained to achieve longer delay times and/or more taps without signal degradation. The limit of how many modules can be chained depends on the integrity of the shared bus signals but 5 modules should be chainable with no additional hardware.
Chained modules are defined by a single Primary module (the PRIMARY input pin is HIGH) and some number of downstream Secondary modules (with the PRIMARY input pin pulled LOW). There can be only a single primary module in a linked system. LINK signals must be connected between the modules as described in this section. A primary module copies its AUDIO_OUTPUT_1 to the Secondary module’s AUDIO_INPUT_1. This is a digital copy so chaining multiple modules does not degrade the audio quality. The Primary module’s analog output 1 is still active and can be used as a delay output as usual. The secondary’s analog input 1 is not used. If desired, 2 channels can be linked by tying the LINK_1CH input pin low on the secondary module. When that pin is LOW, outputs 1 and 2 of the Primary are copied to inputs 1 and 2 of the secondary.
The sampling rate selected on the Primary module will be used on all Secondary modules. Secondary module RATE_0 and RATE_1 input pins are ignored.
There are many possible uses for module chaining. In the simplest case, it can be used to achieve a longer overall delay time than the maximum delay of a single module. If, for example, a delay time of 750ms was desired (3/4 sec) at 48kHz sampling, that exceeds the total delay time of a single module at that sampling rate. A 2-module chain could be used, the first module in the chain could implement a delay with Program 0 and set Tap 1 delay time to 500ms. Tap 1 output is copied to input 1 of the second module via the digital chain. If that module is also running Program 0, then it can add up to 682ms additional delay (it will also be sampling at 48kHz). By setting the MIN/MAX scalars and Tap delay CV signals appropriately, it could add 250ms delay to its Tap 1 output, thus achieving a 750ms delay from input 1 to the first module, to output 1 of the second.
Another use of chaining is to achieve more delay taps (analog audio outputs) than the 4 outputs supported by a single module. More outputs allow for a richer variety of delayed signals to mix, filter and process. Program 5 (MN3011 emulation) uses 2 modules to emulate the 6 taps of the MN3011 BBD chip.
Cumulative Delay
Because downstream modules read their input 1 (and possibly input 2) from upstream (delayed) outputs, delay is cumulative from module to module down the chain. Note that each module is always limited (by program selection) in the total amount of delay it can add, and that if a module changes the delay of Tap 1, that change propagates to all downstream modules. Since each module can be running a different Program, a wide variety in number of delay channels and total delay times can be achieved. Chaining is always limited to passing 1 or 2 audio outputs from one module to the next.
AUDIO_OUT_1 of the upstream modules is copied to input 1 of the downstream module (and possibly out 2 to input 2), but all the analog outputs of the upstream module (including analog outputs 1 and 2) are active and behave according to the selected program. Also note that if a downstream program defines multiple delay channels, only the channel driven from input 1 (and possibly 2) receives data from the upstream module; all other channels of the downstream module run independently within that module and may process completely independent audio signals.
Hardware Configuration
To achieve chaining, one module is designated as the Primary module, all others are Secondary modules. All modules in the chain must be connected together by their LINK_BUS_1 and LINK_BUS_2 pins. On each upstream/downstream pair, the upstream LINK_OUT must be connected to the downstream LINK_IN. These are digital signal lines so PCB layout should be done accordingly. All modules should share a common ground and power supply.

When modules are chained together, the PRIMARY module pin is held HIGH (or unconnected), all others (the Secondary modules) must have the PRIMARY pin held LOW.
All secondary modules in a chain have the analog AUDIO_IN_1 disabled, and audio is instead copied (digitally) from AUDIO_OUT_1 of the nearest upstream module. Depending on the program selected in the downstream module, other analog audio inputs may be active. Module audio chaining is always AUDIO_OUT_1 of the upstream module to AUDIO_IN_1 of the downstream module (and AUDIO_OUT_2 to AUDIO_IN_2 when 2-channel linking is enabled via the LINK_1CH input pin). AUDIO_OUT_1 and AUDIO_OUT_2 may also be used as a normal analog outputs on any of the modules of the chain.
It is also possible for a Primary (or any upstream) module to drive multiple downstream modules, copying its output(s) to the input(s) of more than one downstream module. In this example, the Primary module output 1 is digitally copied to the input 1 of both modules 1a and 1b.
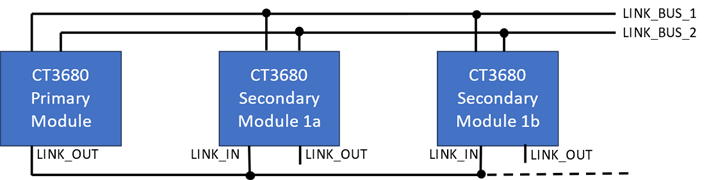
The topology can mix single and multiple downstream modules in a system, but there can be only 1 Primary module, and no more than 5 total.
Chained Programs
Each module in the chain selects its program setting with its own set of PGM input pins (see Program Selection on page 9). It is not required that every module run the same program but note that AUDIO_INPUT_1/2 is disabled on all downstream modules, programs that read input 1 will instead read output 1 of the upstream module as their input. Some programs are designed for multi-modules configurations (e.g. Program 5, the MN3011 emulation program) in which case that program should be selected on all the modules.
In general, it is not required that global MIN/MAX scalars be linked between modules in any particular way. Modules in the chain may each have their own independent scalars, or a single CV can be used to drive the MIN/MAX on multiple modules. Other inputs may or may not be tied together depending on the application.
Typical Applications
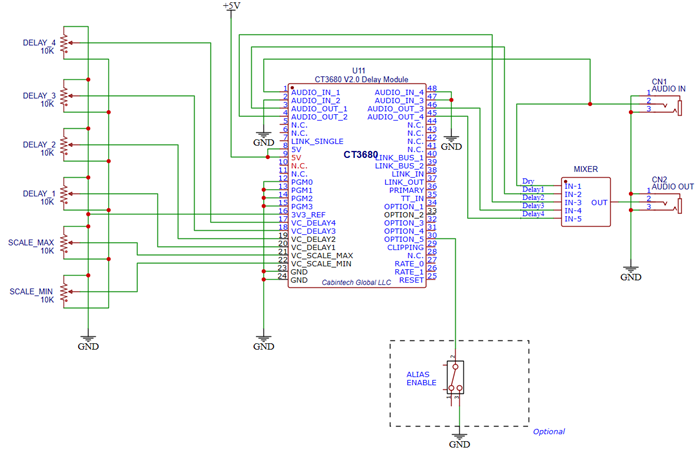
Minimum Reference Schematic
This represents a minimum circuit to implement a 1 line, 4 tap delay with manual (potentiometer) CV controls. For this configuration program 0 is selected (all PGM pins held LOW). The mixer here is conceptual, to show that the original (dry) signal and the various delayed signals might be mixed at various relative levels to produce a single audio output.
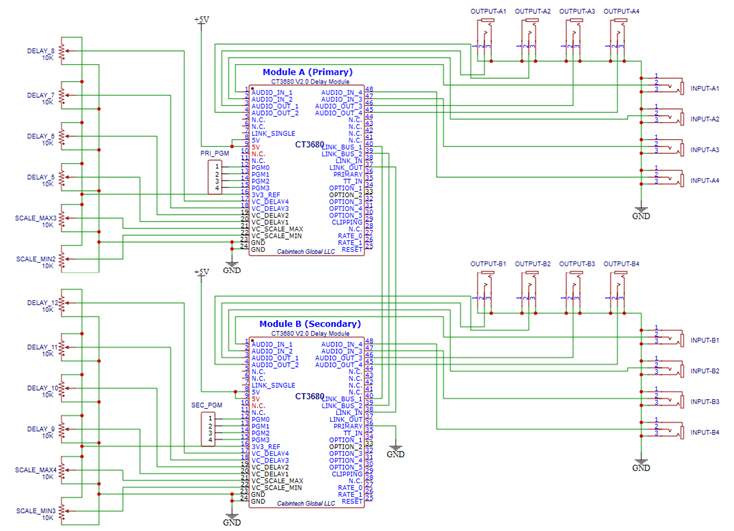
Primary/Secondary Linked Modules
This is a minimum circuit to implement an 8 input, 8 output delay system composed of two linked CT3680 modules with manual CV controls. Both modules should share a common ground and power supply. They may also have shared inputs such as the alias feature controls (OPTION_5, and a CV_DELAY input), depending on the application.
Note the secondary module has the PRIMARY pin tied to ground. Each module is shown with a jumper block to select the program for that module.
Physical Dimensions
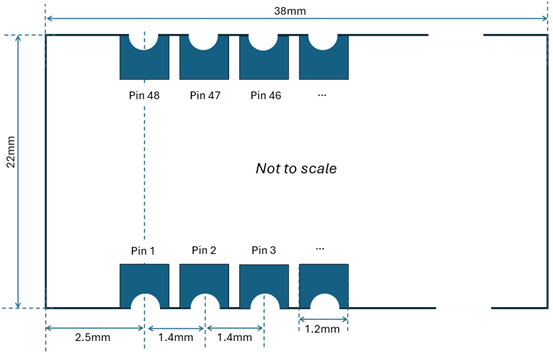
Board dimensions: 38mm (1.5in) x 22mm (0.87in).
Edge pin pitch (spacing): 1.4mm (0.055in)
PCB Design Notes
When designing a PCB on which the CT3680 will be used, note the following guidelines:
1. Adjacent +5 and GND pins should both be connected to the appropriate PCB traces. When possible, use larger track sizes for power and ground connections.
2. Any
pin noted as “N.C.” in the Pinout
section on page 5
should be left unconnected on the PCB. Do not tie these pins to power, ground,
or each other.
3. It
is recommended that a 3 pin header be included on the PCB that provides
connections to pins 10, 11, and GND of the CT3680. These pins can be used to
install firmware updates (see Firmware Updates
on page 31).
Pin 1 of the header should be connected
to pin 11 (I2C_SDA) of the module, pin 2 is GND, and pin 3 should be connected
to pin 10 (I2C_SCL). Production scale
designs that are not intended to be updated can omit this header.
4. Schematic
symbols, PCB footprints, 3D models, and other design resources are available on
the Cabintech website. Symbols and footprints can help avoid errors in the
schematic connections and PCB layout.
Firmware Updates
It is not common, but on occasion it may be useful to update the CT3680 firmware to obtain newly developed programs or enhancements to existing programs. Updating the module firmware requires an FXCore In Circuit Programmer (ICP) board, available on our website. This board provides a bridge between a computer USB port and the CT3680 module. Currently this update process is supported only on Windows 10 or later.
In addition to the ICP, you will need to download the CT3680
updater application from:
https://cabintechglobal.com/apps
Use the link on that page to download the ‘Firmware Updater’. This is a windows EXE that will manage the update process.
Connecting to the Module
You will need access to 3 pins of the CT3680 module (I2C pins 10 and 11) and GND. It is recommended that PCB designs include a 3-pin header for this purpose. The I2C bridge adapter has 3 pins that must be connected to the CT3680. The adapter has markings indicating “SCL” (topmost pin in the photo below), “SDA” (bottom pin), and the center pin is GND. These pins of the adapter must be connected as follows:
|
ICP Adapter |
CT3680 |
|
Pin 3 (top pin) “SCL” |
Pin 10 “I2C_SCL” |
|
Pin 2 (center pin) GND |
GND (Pin 23 or 24) |
|
Pin 1 (bottom pin) “SDA” |
Pin 11 “I2C_SDA” |
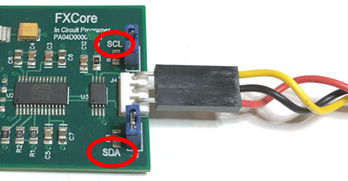
If the PCB on which the CT3680 is mounted has a 3-pin header with these signals, a simple 3-wire cable can be used to connect the adapter to the module. The CT3680 development board has such a header labeled “BURN”.
Running the Updater
The updater (ct3680-updater.exe) is a Windows console
application. Download it to any directory, then open a command window in that
directory and execute it. No administrator privileges are required. The updater
will connect to the Cabintech update service to retrieve the updates and
install them into the CT3680.
Before running the updater, verify:
1.
The Windows PC is connected to the internet.
2.
The CT3680 is powered through its normal power
supply pins (the ICP will not supply power to the CT3680).
3.
The ICP is connected by a USB cable to the
Windows PC.
4.
The ICP is connected to the CT3680 by a 3-pin
cable.
 There
are no parameters or information you need to supply to the updater, just run
the executable from a command window:
There
are no parameters or information you need to supply to the updater, just run
the executable from a command window:
If the updater detects any problems, it will display an
appropriate message. When the updater completes with no errors, the firmware
update is complete to the latest available level.
Development / Breakout Board
A development board is available to aid in prototyping and development of CT3680 based products. The dev board makes all the inputs and outputs of the module accessible through header pins and connectors. The board has 6 potentiometers for manual CV control and switches for setting the program number, option inputs, and other settings. Audio inputs and outputs are available through standard TS (mono) 3.5mm jacks, as well as a TRS (stereo) connector that combines audio outputs 3 and 4. The dev board also has probe points for all pins of the module as well as headers for signals that may be processed off-board.

Development Board Features
· 6 potentiometers for CV controls
· 4 program select switches
· 5 option select switches
· Switches for system sampling rate, and system reset
· Power connector jack
· Power on/off switch and LED
· 8 mono (TS) 3.5mm audio input/output jacks
· 1 stereo (TRS) 2.5mm audio output jack (combines outputs 3+4 into L+R)
· Header pins for all audio inputs and outputs
· 5V, 3.3V, and GND header pins
· Headers for upstream and downstream linked modules
· Switch for 1 or 2 channel linking
· Test points for all pins of the CT3680 module
Power Supply
The power section of the dev board has a 2.1mm power jack (center positive) for +5V power input, an ON/OFF switch, and a LED. The ON/OFF switch allows control of power to the board without removing and inserting the power plug. Double header pins are supplied for off-board access to 5V, 3.3V, and GND. When using multiple development boards it is handy to jumper the 5V supply and GND lines together so only one board needs to have a power plug. Do not tie 3.3V supplies of multiple boards together. Each board generates its own independent 3.3V supply via a regulator on the module.
Program Selection
The board has 4 program selection
switches to allow setting the program via the module’s PGM pins. The program
select lines are also made available on header pins so program selection can be
controlled off-board (for example, by a microcontroller). When driving the
program select lines off-board, the switches must remain in the LOW (off)
position.
Option Selection
The board has 5 selection switches
in the OPTIONS section that allow control of various program options. Header
pins make option control available to an off-board controller. When driving
the option pins off-board, the option switches must remain in the HI position.
System Settings
The SYSTEM section has 2 switches that select one of 4 sampling rates. The legend on the board shows the proper position of the switches for 48kHz, 32kHz, 24kHz, or 12kHz sampling rates. Note that sampling rate changes do not take effect until the system is reset or power cycled. There is a switch in the SYSTEM section to reset the module – turn it briefly from RUN to RESET and back to RUN again.
Delay (CV) Controls
The board has 6 potentiometers along the bottom edge for control of the min/max/1/2/3/4 delay parameters. At the full counterclockwise position, the CV voltage will be 0.0V, full clockwise is 3.3V. The potentiometers are linear. If CV is to be supplied off-board, the CV control jumpers should be removed, and the external CV signals should be supplied to the rightmost pins of the jumper block (closest to the program switches).
![]()

When driving the CV controls from off-board, the CV jumpers must be removed.
Audio Input/Output
3.5mm TS mono jacks are provided for the (4) audio input and (4) audio outputs of the CT3680 module. Each input and output also have a single header pin that is handy for clipping test leads to. There is also a single TRS stereo output jack that combines audio outputs 3/4 into a left/right stereo pair.
Multi-Module Linking
The board has two headers in the LINK section for linking modules as described in Chaining Multiple Modules on page 24. Each header has 4 pins. The primary module development board should have its “DN” (downstream) header connected to the secondary module board’s “UP” (upstream) header. Connect all 4 pins of the header from one board to the next. If a secondary board is to be connected to another secondary board, connect its DN header to the next board’s UP header, and so on, down the chain of boards.
There is a switch in the LINK section to set the module as primary or secondary. There can be only 1 primary module in a chain of modules (see Chaining Multiple Modules on page 24). Changes to the primary/secondary switch only take effect when the system is reset or power cycled. To reset the system, move the switch in the SYSTEM section from RUN to RESET and back to RUN.
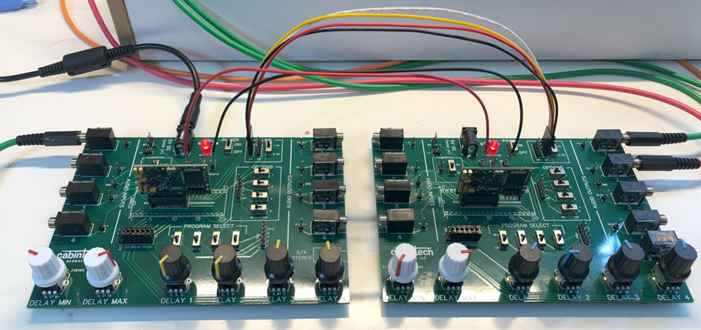
Linked development boards
(Note the photo shows V1 development boards). For secondary module boards, the switch in the LINK section can be set to “1 CH” for single channel linking, or “2 CH” for dual channel linking.
Revisions
|
Rev |
Date |
Changes |
|
Rev 1 |
April 29, 2024 |
First public release |
|
Rev 2 |
May 9, 2024 |
Added Program 6 description (General BBD Emulation) |
|
Rev 3 |
May 13, 2024 |
Updated development board details |
|
Rev 4 |
June 10, 2024 |
Revised for V1.1 of the hardware |
|
Rev 5 |
Aug 12, 2024 |
Revised for V2.0 of the hardware - Castellated edges - I/O pinout changed - Support for multiple sampling rates - Documented header for firmware updating |
Disclaimers
Features and specifications of Cabintech products are subject to change without notice. While Cabintech Global LLC strives to provide accurate and reliable information, no responsibility is assumed for use of its products, infringement of intellectual property, or other rights of third parties as a result of such use.
Cabintech Global LLC assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and applications using Cabintech Global LLC components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
SAFETY-CRITICAL, MILITARY, AND AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS DISCLAIMER: Cabintech Global LLC products are not designed for and must not be used in connection with any applications where the failure of such products would reasonably be expected to result in significant personal injury or death (“Safety-Critical Applications”). Safety-Critical Applications include, without limitation, life support devices and systems, equipment or systems for the operation of nuclear facilities and weapons systems. Cabintech Global LLC products are not designed nor intended for use in military or aerospace applications or environments. Cabintech Global LLC products are not designed nor intended for use in automotive applications.
[1] The delay at an output is the ratio of the CV to 3.3V, multiplied by the delay range (max-min), plus the min. For example, output 1 delay = (0.44V / 3.3V) * (682ms – 0.3ms) + 0.3ms = 91.2ms.
[2] MinDelay + (MaxDelay-MinDelay)*(CVInput/3.3V) = 5.12ms + (51.2ms-5.12ms)*(2.8V/3.3V) = 44.2ms
[3] MaxClock - ((MaxClock-MinClock)*(CVInput/3.3V)) = 100kHz - (100kHz-10kHz)*(2.8V/3.3V) = 23.6kHz