Cabintech CEFX-VCO CEfx Voltage Controlled Oscillator
CEFX-VCO CEFX-VCO Cabintech
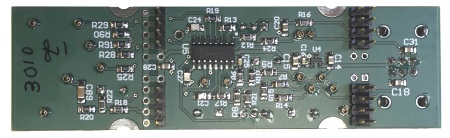
CEFX-VCO cefx vco module synth synthesizer 3340


Loading product data...
A Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) is one of the basic building blocks of a synthesizer. A VCO produces alternating outputs
in several waveforms with the frequency (tone) controlled by an input voltage. The higher the input voltage, the higher the
output frequency. The input voltage might come from a manual source like a knob, from an instrument like a keyboard, from another
synth module, or some esoteric control surface.
This CEfx VCO module is based on the Coolaudio V3340M Voltage-Controlled Oscillator. It features standard 1V-per-octave
tuning, and has three simultaneous outputs: triangle, ramp, and pulse, with a manual- or voltage-controlled pulse width.
Outputs all range from 0V to +4V. We expect to offer a companion triangle-to-sine converter module soon. Note that outputs are not buffered.
Output impedance is 10K for triangle out, 5K for ramp out, and 3.6K for pulse out.
Features
- Based on the Coolaudio V3340 VCO chip
- Triangle, ramp, and pluse outputs
- Two summed CV inputs plus on-board frequency offset pot
- Socketed frequency range capacitor can be swapped out to create a LFO
- FM input
More CEfx Information
Powering CEfx Modules
CEfx Mounting Options
CEfx Breadboards
Usage Notes
The testpoints labeled "CV1 IN" and "CV2 IN" are two identical control voltage inputs that get summed together, so you can put a keyboard output into CV1 and an LFO into CV2.
A third CV input is hard-wired to the "FREQ OFFSET" pot, which adds up to 5V (5 octaves) to the base frequency.
You can also jumper one of the CV IN testpoints to one of the nearby +5VREF testpoints to add 5 octaves to the range. Or you can connect a potentiometer
or other variable resistance between the +5VREF pin and a nearby GND to create control voltages.
For voltage controlled pulse-width modulation, remove the jumper labeled PWM and inject a control voltage between 0V and +5V into the testpoint closest to trim pot R11.
C23 (the socketed capacitor) determines the frequency range of the VCO. The standard CEfx-VCO uses a 100pF capacitor here to set the base frequency range
(adjusting FREQ offset with no external CV) to roughly 8 Hz to 220 Hz. You can easily turn the module into an LFO by replacing C23 with a higher-value capacitor.
0.1uF is a good choice for an LFO. Use a film capacitor here, not a ceramic, for frequency stability.
The FM input is DC-blocked, and accepts CV signals above 1 Hz and up to +/-10V, or audio at frequencies up to the VCO's output frequency.
Calibration Process
It may be desirable to calibrate the VCO to produce very specific frequencies for very specific input control voltages. In particular
you may want to produce standard musical notes (e.g. middle C at 261.6Hz) for a particular input voltage.
There are lots of possible calibration protocols, but this is the procedure that we used to calibrate the CEfx-VCO:
- Apply a calibrated source of 1.000V to CV1 in.
- Read pulse output on a frequency counter.
- Adjust manual offset until frequency counter reads 200Hz.
- Change voltage source to 2.000V.
- Frequency should read 400 Hz. If its low, turn "8va TUNE" clockwise. If its high, turn counterclockwise.
- Change voltage source back to 1.000V and readjust manual offset until frequency reads 200 Hz.
- Continue toggling between 1V and 2V, adjusting the manual offset and the 8va tune until you get to 200 and 400 Hz.
- Change voltage source to 3.00 V and verify frequency of 800 Hz. It may be necessary to tweak the 8va TUNE pot for a more accurate reading. As you
check higher octaves, you will need to adjust the "HV TRACK" pot for the higher octaves, then go back and re-measure the lower octaves,
then re-tweak the 8va TUNE pot.
Design Notes
This is a basic Coolaudio V3340 design in which we wanted to expose as much functionality as possible while keeping the design reasonably simple and understandable.
- A few minor tweaks were made for +/-12V operation and we adjusted the output voltage dividers so that all three waveforms would go from 0V to +4V.
- A hysteresis resistor between pins 4 and 5: 2.5 MOhm was the value needed to stop square wave glitches
- Outputs are not buffered (trying to keep things simple), but the result is fairly high output impedances, so watch out for that (cannot drive a lot of load).
- This design does not allow for hard or soft sync inputs, in the name of simplicity, but if there's enough interest, we might try to add some hooks in a future rev.
- Using a breadboard friendly audio jack makes it easier to receive CV signals from an external controller (such as a keyboard that has CV outputs).
- Some ideas for enhancing this on your breadboard:
- Individual op-amp buffers on all outputs
- Triangle-sine converter
Schematic
Download Schematic PDF

News: Facebook page.
Reviews: Trustpilot
Home
Semiconductors
Articles
CEfx Experimenters Series Modules
About Us
Contact Us
V 12.43


 Loading product data...
Loading product data...


